Human exposure to heavy metals has risen dramatically in the last 50 years. Many of the elements that can be considered heavy metals have no known benefit for human physiology. Lead, mercury, and cadmium are prime examples of such "toxic metals." Any of these elements may have pernicious effects if taken in quantity or if the usual mechanisms of elimination are impaired.
With the possible exceptions of acute iron toxicity from intentional or unintentional ingestion and suspected lead toxicity, emergency physicians will rarely be alerted to the possibility of metal exposure. Yet, if unrecognized or inappropriately treated, heavy metal exposure can result in significant morbidity and mortality.
Exposure to metals may occur through the diet, from medications, from the environment, or in the course of work or play. Where heavy metal toxicity is suspected, time taken to perform a thorough dietary, occupational, and recreational history is time well spent, since identification and removal of the source of exposure is frequently the only therapy required.
Chronic occupational exposure to metal dusts has also been linked to the development of pneumoconioses, neuropathies, hepatorenal degeneration and a variety of cancers. These syndromes develop slowly over time and may be difficult to recognize clinically. In the United States, Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) regulations guide the surveillance of workers at risk and suggest exposure limits for metals of industrial importance.
Todays Chronic Exposure may come from:
-
Mercury-amalgam dental fillings
-
Lead Paint
-
Tap Water
-
Chemical Residues in Processed Foods
-
Personal Products (Cosmetics, Shampoo, hair products, Mouthwash, toothpaste, soap, etc.
Many occupations involve daily heavy metal exposure over 50 professions entail mercury exposure alone
-
Physicians and Dental Workers
-
Car or Boat Repair
-
Home Remodeling
-
Hairdressers and Cosmetic Workers
-
Painters and Potters
-
Printers, Visual Artists and Photographers
-
Welders, Engravers and Metal workers
-
Battery makers, Gas station attendants
Chelation therapy through the use of Calcium Disodium EDTA is a popular modality for the removal of toxic metals, especially for lead from the body. The FDA approves EDTA for the treatment of heavy metal toxicity. This was first introduced into the US in 1948 as a treatment for the lead poisoning of workers in a batter factory. Shortly thereafter, the US Navy advocated chelation for sailors who had absorbed lead whole painting government ships and facilities.
Atherosclerosis affects medium and large sized arteries. General occlusion is a slow process, and gradually progresses until it becomes manifest in clinical symptoms after the lumen is 75% occluded. Plaque is mostly cholesterol complexed to proteins with calcium to act as the “glue”, with as much as 40% of the dry weight being attributed to calcium. Plaque can lead to total vascular occlusion resulting from from calcification, emboli formation, thrombus formation and internal hemorrhage.
A search of medical literature for EDTA chelation therapy related to improvement in vascular disease by objective testing before and after treatment, lead to 19 articles that met the criteria with a cohort of 22,765 patients. Of the 22,765 patients treated, an 87% improvement in vascular disease was derived, with a correlation coefficient of 0.88(high). Furthermore, according to Hanckes data, EDTA treatment might have prevented 363,000 of the 407,000 bypass procedures done in the US in 1991, saving more than $8 billion dollars.
Chelation therapy with EDTA can help remove aluminum from the brain, a metal that contributes to Alzheimers Disease. According to Drs. H. Richard Casdorph and Morton Walkers, authors of Toxic Metal Syndrome: How Metal Poisoning Can Affect your Brain, chelation therapy has been shown to help in patients with early-stage Alzheimers. It has also been documented as showing greater clarity, improved memory, and increased IQ.
It has been postulated that chelation therapy helps to control free radicals which are linked to the cell destruction that can lead to cancer. Walter Blumer, MD of Switzerland conducted a study which started in 1958 and investigated 231 adults who lived near a well travelled highway. Living near this highway had a higher rate of cancer deaths than people in the same city who lived in areas with less traffic. It was speculated that the higher rate of cancer was linked to the greater exposure to lead form the automobile exhaust. Of the 231 people (105 men, 126 women), 31 (17 men, 14 women) died of malignant tumors during the 18-year observation (1959-1976). Twenty-eight of the deceased had lived for more than 10 years directly adjacent to the highway and were normally present in their homes for 24 hours every day.
From 1959-1976, 59 people from this group underwent 10 or more EDTA chelation treatments with Vitamin C and B1. One died of cancer (1.7%). Of the other 172 untreated control subjects who had not received EDTA, 30 (17.4%) died of cancer. Analysis of occupational data and location during the day showed no differenced between the two groups
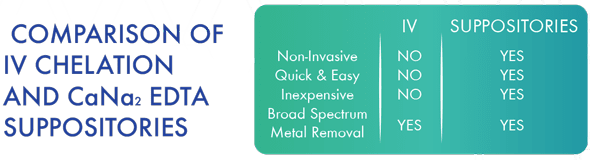
Fortunately, an alternative delivery method has opened up the whole world of heavy metal detoxification, making it available to everyone. EDTA Chelation Suppositories are chemically equivalent to the traditional IV EDTA chelation method and eliminate many of the shortcomings that are associated with IV EDTA delivery. The very same ingredient that goes into the IV (CaNa2EDTA or calcium disodium EDTA) has been incorporated into rectal suppositories. The dosage is smaller so that it does not put so much strain on the body, especially the kidneys. Each suppository can contain up to 750mg of calcium disodium EDTA (about a quarter of regular IV dosage), which is slowly absorbed through the sigmoid colon while asleep and gently works to detoxify the body of heavy metals such as lead and mercury. This delivery method altogether avoids the disadvantages associated with traditional IV chelation. It has been praised as a very effective chelation system and is readily used as a delivery system by physicians and consumers worldwide.
-
Take one EDTA Suppository rectally every other night prior to bedtime
-
Take a good multivitamin and mineral daily
-
Drink plenty of water and stay well hydrated with at least 100oz per day
Chelation therapy works best when integrated with a good diet, nutrients and lifestyle changes. A thorough evaluation of each patient by a medical doctor should be performed including a heavy metal screening, and an individualized nutritional program is prescribed.
If a patient has never detoxified with chelation therapy in the past, it is recommended to use the EDTA suppositories as described above for at least 6 months. After this initial program, it is recommended to continue using one suppository every week thereafter as on-going maintenance for detoxification of heavy metals.
Assuming that there are not any liver or kidney issues, Dr. Rita Ellithorpe, author of Detox Outside the Box, recommends EDTA suppositories at three dosage levels: 375mg for people under 45kg, 750mg for people between 45kg-80kg, and 1000mg for people over 80kg.
-
Rapid onset malaise, fatigue and excessive thrust followed by fevers and chillsfurther followed myalgia, frontal headaches, anorexia, occasional nausea & vomiting
-
Histamine like reaction
-
Sneezing, nasal congestion and lacrimation
-
Transient Hypocalcemia
-
Allergy to EDTA
-
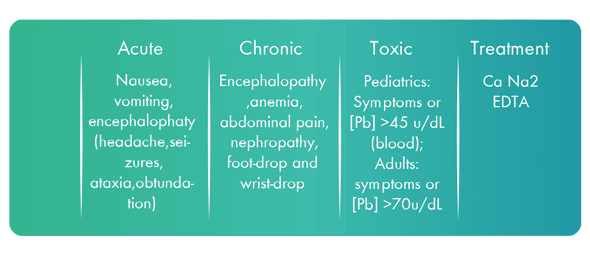
Acute lead encephalopathy
-
Renal Dialysis
-
Moderate Renal Insufficiency- (Serum Creatinine of 2-2.5mg/dl)
Renal Impairment --(Serum Creatinine of 1.6-2.0mg/dl) Patients with mild renal insufficiency may be able to tolerate EDTA chelation therapy well, but their renal function should be monitored closely.
Active Liver Disease --such as Hepatitis A, B, C or Cirrhosis where there are elevated levels of liver enzymes, bilirubin, decreased plasma proteins or increased prothrombin times secondary to active liver disease.
Anticoagulation --Patients on long term anticoagulation with Coumadin should have the prothrombin times monitored closely as EDTA may alter prothrombin times and require Coumadin dose changes
Patients with a history of recurrent life threatening DVT or embolic phenomena related to a cardiac source with concomitant Atrial Fibrillation
Congestive Heart Failure --EDTA may lower serum calcium resulting in a reduced iontropic effect on themyocardium which may result in a sudden exacerbation of CHF in a very small portion of that population
Pregnancy --Has not been tested in pregnancy
For more information contact us
- Phone: (949) 642-0106
- |
- Fax: (949) 642-5039




